Comprehensive Guide to Food and Beverage Distribution
Dive into an in-depth overview of the food and beverage distribution industry. This guide covers everything from supply chain logistics to technological optimization and best practices, providing you with the tools you need to succeed.

What Global Brands Do We Serve?






When Should You Read This Guide?
The need to modernize traditional distribution models is becoming increasingly evident due to challenges such as:
- Enhanced Efficiency: Streamlining operations to cope with increased demands, allowing for quicker responses and reduced costs.
- Increased Transparency: Implementing systems for real-time tracking and updates, ensuring accountability and building customer trust.
- Adaptability to Industry Trends: Embracing initiatives such as sustainability and digital transformation to remain competitive.
Whether you're just starting your journey in food and beverage distribution or you’re an experienced professional looking to optimize your operations, this comprehensive guide is tailored for you. It offers valuable insights that cater to all levels of expertise.

Why Should You Read It?
Understanding the complexities of food and beverage distribution is crucial for enhancing operational efficiency, improving customer satisfaction, and staying competitive in a rapidly evolving market. This guide offers expert insights, strategies, and real-world case studies, including a spotlight on Baldor Specialty Foods, to help you navigate challenges and seize opportunities in the industry.
- 70% of food distributors report improved efficiency after implementing route optimization software.
- 60% of customers prefer real-time tracking for their deliveries.
- Companies that adopt advanced inventory management systems see a 30% reduction in stockouts.
Who Should Read This?
This guide is essential for:

Food Service Distributors

Broadline & Specialty Distributors

Beverage Distributors

Hybrid Model Operators
Are You Ready to Transform Your Distribution Operations?
Start reading our comprehensive guide today and discover how to elevate your food and beverage distribution strategies!
Overview
What is Food and Beverage Distribution?
What are the Key Challenges in the Supply Chain?
What is the Role of Technology in Distribution?
What are the Best Practices for Food Service Distribution?
Why are Visibility Solutions Important in the Supply Chain?
What Makes Baldor Specialty Foods a Successful Case Study in Food and Beverage Distribution?
What are the Future Trends in Food and Beverage Distribution?
Comprehensive Guide to Food and Beverage Distribution
The food and beverage distribution industry is a cornerstone of the global supply chain, tasked with the critical role of moving products from manufacturers to retailers and ultimately to consumers. This guide offers an in-depth exploration of the industry's complexities, covering essential topics such as supply chain logistics, technological advancements, and best practices that drive success. We begin by providing an overview of food and beverage distribution, examining the roles and responsibilities of distributors and the challenges they face, from logistical hurdles to regulatory compliance. The transformative impact of technology is highlighted, showcasing how innovations like ORTEC B2B delivery solutions have enhanced operational efficiency and reduced costs. Additionally, we emphasize the importance of adopting best practices, such as focusing on customer service and integrating technology, to maintain high standards of service and operational excellence.
The guide also delves into the significance of visibility solutions in supply chain management, exploring tools that enhance visibility and their impact on decision-making and operations. A case study on Baldor Specialty Foods illustrates how a focus on specialty products and customer service can lead to food distribution success. Looking to the future, we identify trends that will shape the food service industry, including advanced forecasting, automation, and sustainability initiatives. These insights provide valuable guidance for industry professionals seeking to navigate the complexities of the food and beverage distribution sector, offering strategies to enhance efficiency, customer satisfaction, and competitive advantage.
What is Food and Beverage Distribution?
The food and beverage distribution industry is a critical component of the global supply chain, serving as the intermediary between manufacturers and the end retail points, such as hotels, restaurants, grocery stores, and other food service providers. This chapter provides an overview of the food and beverage distribution sector, highlighting its structure, functions, and the complexities involved.
Understanding Food and Beverage Distribution
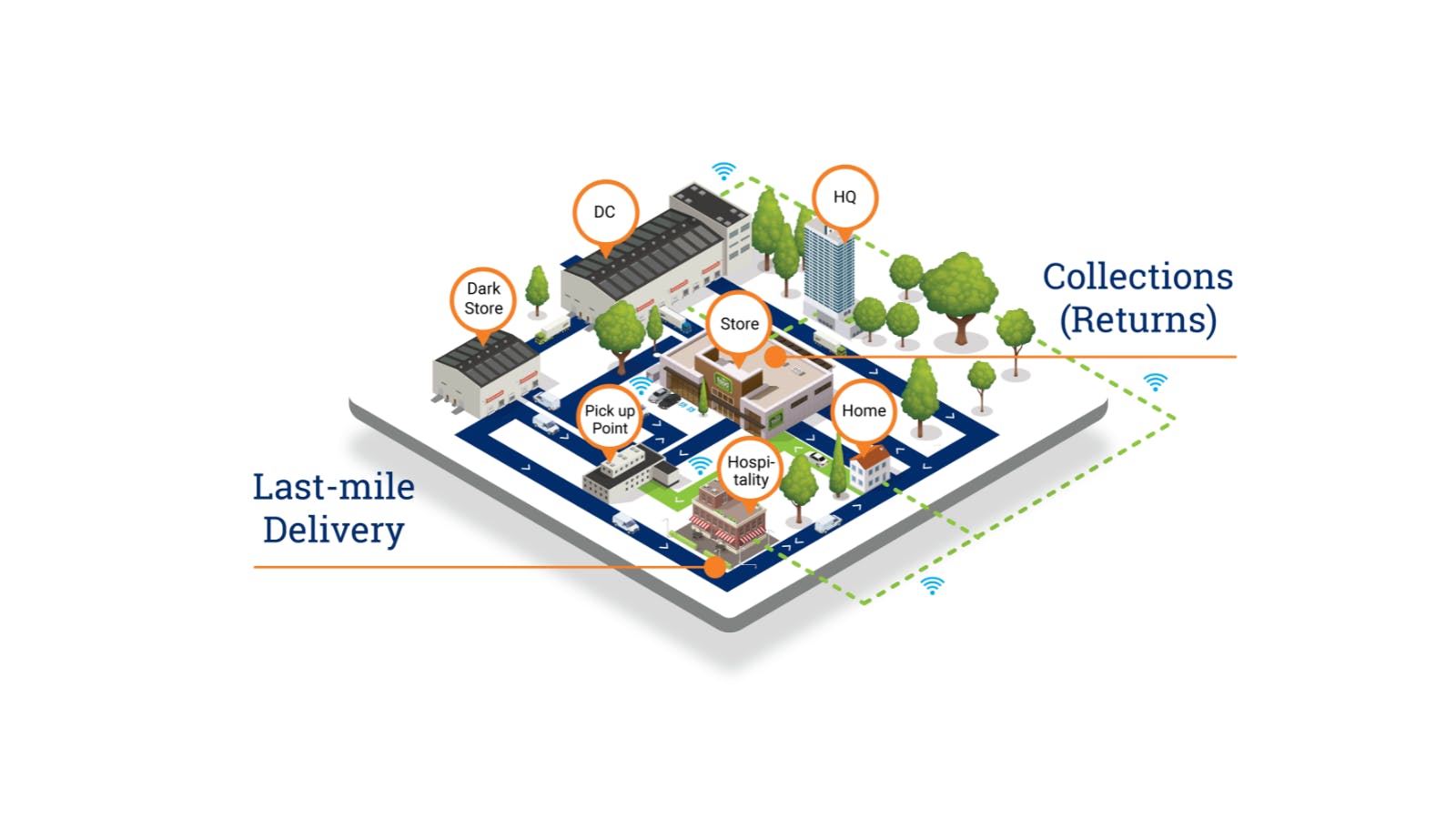
Food and beverage distribution involves the delivery of products from manufacturers to various businesses, including hotels, restaurants, grocery stores, convenience stores, and caterers. These distributors play a pivotal role in ensuring that products reach their final destinations efficiently and in optimal condition. They also cater to institutional customers such as schools, and homes for the elderly, showcasing the diverse range of clients they serve.
Distinction Between Food and Beverage Distribution
The distribution sector can be divided into two main categories: food distribution and beverage distribution. On the food side, distributors focus on food service distribution, handling a wide range of products. In contrast, beverage distribution often involves a mixed model where beverage and snack manufacturers manage their own distribution networks, sometimes alongside independent wholesalers. This dual approach is also seen in the beer industry, where companies use both their own trucks and external wholesalers.
Hybrid Models in Distribution
Some companies adopt hybrid distribution models to optimize their operations. For instance, a large retailer in Australia, through its subsidiary, manages wine distribution by importing some products while relying on domestic wholesalers for others. This flexibility allows companies to tailor their distribution strategies to specific market needs and product types.
Broadline vs. Specialty Distribution
In the food industry, distribution can be further categorized into broadline and specialty. Broadline distributors, , handle a wide array of regular products like potatoes and chicken. Specialty distributors, like Baldor Specialty Foods, focus on niche markets, offering organic and farm-raised products. These specialty distributors often have separate supply chains due to different sourcing requirements and smaller volumes, catering to customers willing to pay a premium for unique offerings.
Primary Functions of Distributors
Distributors in the food and beverage industry are responsible for a multitude of functions:
- Purchasing and Inventory Management: Distributors purchase goods and manage inventory in their warehouses, ensuring a steady supply of products.
- Logistics and Transportation: They handle the logistics of moving products from warehouses to customers, ensuring timely and efficient delivery.
- Order Management: Distributors receive and process orders from customers, coordinating the entire order fulfillment process.
- Value-Added Services: Some distributors offer additional services such as portioning, special labeling, or packaging, enhancing the value they provide to customers.
- Merchandising: In certain cases, distributors employ merchandisers to ensure products are displayed attractively in retail outlets, a common practice in the beverage sector.
The Complexity of Distribution
The distribution process is inherently complex, involving multiple stakeholders and intricate logistics. While beverage distribution by manufacturers may seem straightforward, the broader wholesale distribution landscape is more intricate. Food distribution, in particular, presents unique challenges due to the diversity of products and the need for specialized handling and storage.
In conclusion, the food and beverage distribution industry is a vital link in the supply chain, bridging the gap between manufacturers and consumers. Its complexity and diversity require distributors to be adept at managing logistics, inventory, and customer relationships. As the industry continues to evolve, understanding these foundational elements is crucial for navigating the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead
What are the Key Challenges in the Supply Chain?
The food and beverage supply chain is a complex network that faces numerous challenges, impacting efficiency, service quality, and profitability. This chapter delves into the primary obstacles that industry players encounter and explores strategies to overcome them.
Distinct Challenges in Food and Beverage Distribution
The food and beverage sectors, while interconnected, face unique challenges due to their distinct operational requirements.
Challenges in the Food Industry
- Highly Competitive Market: The food services industry, particularly broadline distribution, is highly competitive. Distributors often compete on service rather than product differentiation, as commodities like potatoes or chicken are similar across suppliers. This necessitates a focus on customer service, on-time delivery, and enhancing the customer experience.
- Logistical Complexities: Food distribution involves handling diverse products with specific storage and transportation needs. For instance, frozen items like chicken and French fries require specialized vehicles and storage facilities. Additionally, unique SKUs for large fast-food chains complicate distribution due to limited storage locations.
- Unionization and Labor Challenges: Unionization presents challenges related to driver preferences and legal requirements. Staffing shortages, particularly in warehouses, exacerbate these issues, as companies strive to maintain service levels while managing costs.
- Cold Chain and Food Safety: Compliance with cold chain regulations is crucial to ensure food safety. Distributors must navigate stringent regulations while managing margin pressures and intense competition.
- Technological Integration: Many food distributors have evolved from family businesses with legacy systems. Integrating modern technology to streamline operations, enhance order processing, and improve connectivity with partners is a significant challenge.
Challenges in the Beverage Industry
- Loading and Routing Complexities: Beverage distribution involves diverse products, requiring careful loading and routing to prevent damage (e.g., avoiding placing heavy kegs on fragile six-packs and considering bay preferences). Efficient loading strategies are essential to optimize delivery routes and minimize costs.
- Merchandising: Beverage distributors often employ merchandisers to ensure products are attractively displayed in stores. This adds a layer of complexity, as it involves coordinating field services and routing to maximize efficiency.
- Seasonal Fluctuations: Both food and beverage sectors experience significant seasonal demand fluctuations, particularly during holidays like Thanksgiving and Christmas. These periods require strategic planning to manage increased volumes and staffing challenges.
Strategies to Overcome Supply Chain Challenges
- Operational Flexibility and Proactive Planning: Companies must adopt a flexible approach to operations, allowing for dynamic adjustments based on demand fluctuations. Proactive planning, including forecasting and scenario management, will help anticipate and mitigate the impact of seasonal changes.
- Technology Integration: Embracing modern technology solutions can streamline operations, improve order accuracy, and enhance connectivity with partners. This includes leveraging tools for route optimization, inventory management, and customer relationship management.
- Strategic Alignment: Organizations should align their supply chain strategies with overall business goals. This involves evaluating business rules and constraints, many of which may be outdated, and adopting a more dynamic approach to operations.
- Focus on Efficiency and Service: By optimizing logistics and focusing on customer service, distributors can differentiate themselves in a competitive market. This includes improving delivery accuracy, reducing lead times, and enhancing the overall customer experience.
- Forecasting and Capacity Planning: Accurate forecasting is essential for managing demand volatility and optimizing resource allocation. Companies should develop strategies to balance capacity, ensuring they can meet demand without incurring unnecessary costs.
In summary, the food and beverage supply chain faces a myriad of challenges, from logistical complexities to seasonal demand fluctuations. By adopting a proactive and flexible approach, leveraging technology, and aligning strategies with business goals, distributors can navigate these challenges and enhance their competitive edge. As the industry continues to evolve, staying ahead of these challenges will be crucial for sustained success.
What is the Role of Technology in Distribution?
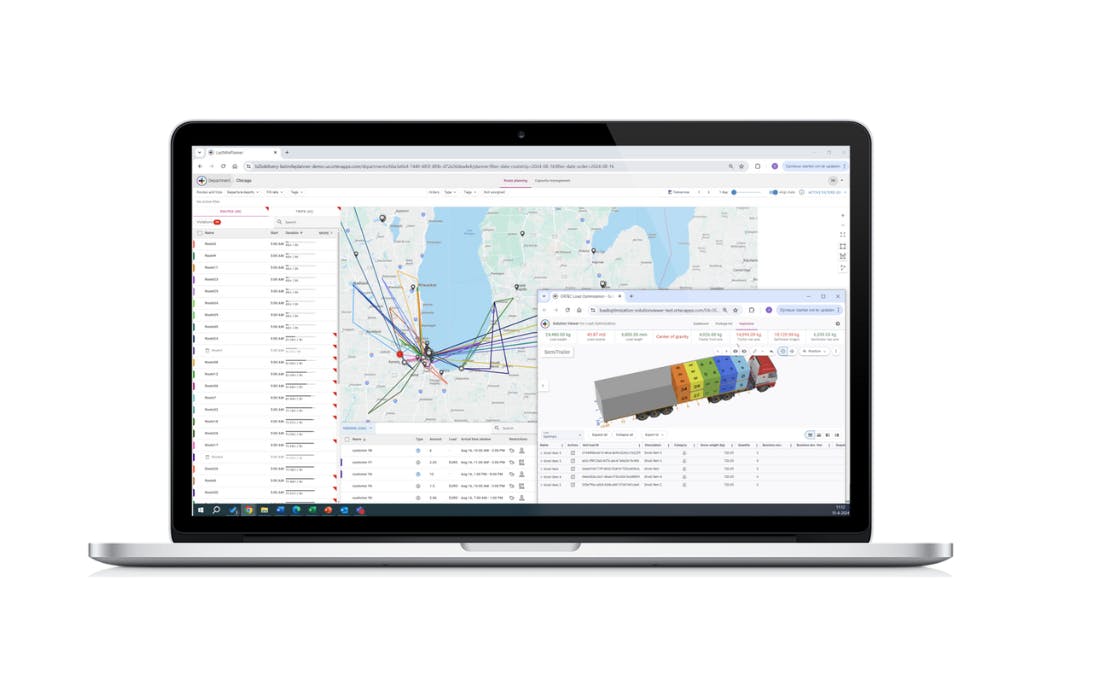
In the rapidly evolving landscape of food and beverage distribution, technology plays a pivotal role in transforming operations, enhancing efficiency, and reducing costs. This chapter explores how technological advancements, such as ORTEC B2B delivery solutions, have revolutionized the distribution process, while also considering potential drawbacks and limitations.
Transformative Impact of Technology
- Route Optimization: One of the most significant technological advancements in distribution is route optimization. Solutions like ORTEC B2B delivery enable companies to efficiently plan and execute delivery routes, balancing static and dynamic components. This technology helps determine which routes should remain constant and which can be adjusted in real-time, ensuring optimal resource utilization and timely deliveries.
- Forecasting and Planning: Technology facilitates accurate forecasting and strategic planning, allowing distributors to anticipate demand fluctuations and adjust operations accordingly. This capability is crucial for managing seasonal peaks and ensuring that resources are allocated efficiently.
- Intelligent Process Management: Technology enables more intelligent management of static components within the distribution process. By leveraging data analytics, companies can identify when updates to territories, bidding processes, and other setups are necessary, removing traditional boundaries and enhancing operational agility.
- Efficiency and Speed: Technological solutions streamline information flow, making processes faster and easier. For instance, focussing on overlapping loading crews and routing processes exemplifies how technology can enhance service levels and efficiency by ensuring that routes are ready for execution as soon as possible.
- Frequency Optimization: Over time, customer delivery patterns may change, leading to inefficiencies. Technology allows distributors to review and optimize delivery frequencies, reducing unnecessary visits and improving overall efficiency.
Examples of Technological Benefits
- Case Study: By integrating technology into their distribution model, this ORTEC customer improved service levels and efficiency. The ability to quickly adapt routes and streamline loading processes resulted in faster truck dispatches and enhanced customer satisfaction.
- Frequency Optimization: Distributors can use technology to analyze delivery patterns and identify opportunities for consolidation. For example, a restaurant initially receiving deliveries twice a week may no longer require such frequency, allowing for more efficient scheduling.
Potential Drawbacks and Limitations
While technology offers numerous benefits, there are potential drawbacks and limitations to consider:
- Adoption Challenges: Successful implementation of technology requires widespread adoption across the organization. Resistance to change or inadequate training can hinder the effectiveness of new systems.
- Dependence on Technology: Over-reliance on technology can be problematic if systems fail or become outdated. Ensuring that technology solutions are robust, reliable, and regularly updated is essential to avoid disruptions.
- Complexity and Usability: Poorly designed technology can create more problems than it solves. Solutions must be user-friendly and fit for purpose, ensuring that they enhance rather than complicate operations.
To conclude, technology is a driving force in the transformation of food and beverage distribution, offering solutions that enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve service levels. By leveraging tools like route optimization, forecasting, and intelligent process management, distributors can navigate the complexities of the supply chain with greater agility and precision. However, successful implementation requires careful consideration of potential drawbacks and a commitment to continuous improvement and adaptation. As the industry continues to evolve, embracing technology will be crucial for maintaining a competitive edge and meeting the demands of an ever-changing market.
Technology is a driving force in the transformation of food and beverage distribution, offering solutions that enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve service levels.
What are the Best Practices for Food Service Distribution?
In the competitive landscape of food service distribution, adhering to best practices is essential for maintaining efficiency, ensuring quality, and enhancing customer satisfaction. This chapter explores the key practices that successful distributors follow to excel in the industry.
Key Best Practices
- Focus on Cost and Customer Service: At the heart of successful foodservice distribution is a dual focus on cost management and exceptional customer service. Distributors often provide a commodity, and growing the business hinges on delivering outstanding service. This includes ensuring on-time delivery, maintaining open communication with customers, and upholding safety and quality standards.
- Vehicle and Product Management: Proper vehicle maintenance and loading are crucial. Vehicles must be in good condition, loaded correctly, and capable of maintaining the required temperatures for different products. Informing customers of delivery times and ensuring that drivers are well-trained and customer-oriented are also vital components of effective distribution.
- Adherence to Regulations: Distributors must navigate various regulations, such as weight limits and access restrictions, which can vary by country or region. While these rules can be seen as constraints, successful distributors view them as manageable challenges that must be addressed to ensure compliance and smooth operations.
- Technology Integration: Leveraging technology is a best practice that cannot be overlooked. Integrating e-commerce portals with inventory, warehouse management, and route planning systems enhances efficiency and customer satisfaction. Technology enables distributors to streamline operations, optimize routes, and provide customers with real-time information.
- Quality and Safety Assurance: Ensuring the quality and safety of food products is paramount. This involves maintaining proper temperature control, often managed with IoT devices on trucks and in warehouses. While technology can provide monitoring capabilities, the responsibility for maintaining these standards lies with the distributors.
- Customer Service Excellence: Customer service is the cornerstone of effective distribution. It involves delivering orders on time, in full, and in the right conditions. Distributors can enhance customer service by allowing customers to select delivery slots and using smart route optimization to meet these preferences. The human element, such as drivers' interactions with customers, plays a significant role in building strong relationships and ensuring repeat business.
The Role of Customer Service
Customer service is not just a component of beverage and food distribution; it is the driving force behind successful operations. From the customer's perspective, receiving orders on time and in perfect condition is paramount. Distributors must ensure that their processes and technologies support this goal.
- Empowering Customers: Allowing customers to choose delivery slots and ensuring timely deliveries through route optimization are ways to enhance customer satisfaction.
- Balancing Efficiency and Service: While technology can improve efficiency, it must be used wisely to avoid compromising customer service. For example, reducing stop times to increase efficiency should not lead to rushed or unprofessional behavior during deliveries. Distributors must ensure that technology supports, rather than hinders, the human touch that is often crucial in customer interactions.
To wrap up, best practices in food service and beverage distribution revolve around a commitment to cost management, customer service, regulatory compliance, and technology integration. By focusing on these areas, distributors can navigate the complexities of the industry and deliver exceptional value to their customers. As the industry continues to evolve, maintaining a balance between efficiency and personalized service will be key to sustaining success and fostering long-term customer relationships.
Why are Visibility Solutions Important in the Supply Chain?
In the food and beverage distribution industry, supply chain visibility is a critical factor that influences efficiency, customer satisfaction, and operational decision-making. This chapter explores why visibility is crucial, the tools available to enhance it, and the impact improved visibility has on operations.
Why Visibility is Crucial
- Enhanced Customer Service: Visibility in the supply chain allows distributors to provide customers with real-time information about their orders. This includes tracking the journey of products, estimated arrival times, and delivery status. By offering transparency, distributors can improve customer satisfaction and build trust.
- Operational Efficiency: Internal visibility enables distributors to monitor the progress of deliveries and manage exceptions effectively. By identifying potential issues, such as delays or driver shortages, companies can take proactive measures to mitigate disruptions and ensure timely deliveries.
- Risk Management: Visibility helps distributors anticipate and respond to potential risks in the supply chain. Whether it's a vehicle breakdown or a delay due to traffic, having real-time data allows for quick decision-making and contingency planning.
Tools and Solutions for Enhancing Visibility
- Mobile Devices and GPS: Many distributors equip drivers with mobile devices that have scanning capabilities and GPS tracking. These devices provide real-time data on the location and status of deliveries, enabling both internal and external visibility.
- Vehicle-Installed Devices: Some companies use devices installed directly on vehicles to track their movements and monitor delivery progress. These tools provide accurate data on vehicle location, speed, and route adherence.
- Visibility Platforms: Advanced software solutions offer comprehensive visibility across the supply chain. These platforms integrate data from various sources, providing a centralized view of operations and enabling better coordination and communication.
- Customer-Facing Apps: To enhance external visibility, distributors can offer customer-facing apps that provide real-time updates on delivery status. These apps empower customers with information, reducing the need for manual inquiries and improving the overall service experience.
Impact of Improved Visibility on Decision-Making and Operations
- Informed Decision-Making: With enhanced visibility, distributors can make informed decisions based on real-time data. This includes optimizing routes, reallocating resources, and adjusting delivery schedules to meet customer demands.
- Proactive Issue Resolution: Improved visibility allows for management by exception, where potential issues are identified and addressed before they escalate. This proactive approach minimizes disruptions and ensures that operations run smoothly.
- Increased Accountability: Visibility solutions provide a clear record of delivery activities, increasing accountability among drivers and operational staff. This transparency helps identify areas for improvement and fosters a culture of continuous enhancement.
- Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty: By providing customers with accurate and timely information, distributors can enhance the customer experience, leading to increased satisfaction and loyalty. Customers appreciate the transparency and reliability that visibility solutions offer.
Overall, visibility in the supply chain is a vital component of successful food and beverage distribution. By leveraging technology to enhance visibility, distributors can improve customer service, optimize operations, and make informed decisions that drive efficiency and growth. As the industry continues to evolve, investing in visibility solutions will be essential for maintaining a competitive edge and meeting the ever-changing demands of the market.
What Makes Baldor Specialty Foods a Successful Case Study in Food and Beverage Distribution?
Case Study: Baldor Specialty Foods and Distribution Success
Baldor Specialty Foods stands out as a successful case study in the food distribution industry due to its focus on delivering high-quality, specialty products and its ability to adapt to the unique demands of its market. As a distributor specializing in organic and farm-raised products, Baldor has carved out a niche by catering to customers who are willing to pay a premium for unique offerings. This focus on specialty products allows Baldor to differentiate itself from broadline distributors and build strong relationships with its customer base.
What Specific Strategies or Innovations Has Baldor Implemented to Achieve Success?
- Specialty Product Focus: Baldor's emphasis on organic and farm-raised products has allowed it to target a specific segment of the market that values quality and sustainability. By sourcing unique products and maintaining high standards, Baldor meets the expectations of discerning customers.
- Split Supply Chains: Recognizing the different sourcing requirements and smaller volumes associated with specialty products, Baldor has implemented split supply chains. This approach ensures that the unique needs of specialty products are met, from sourcing to delivery, while maintaining efficiency.
- Customer-Centric Approach: Baldor places a strong emphasis on customer service, ensuring that its products are delivered on time and in optimal condition. By focusing on customer satisfaction and building strong relationships, Baldor has been able to retain and grow its customer base.
How Can Other Distributors Learn from Baldor's Approach?
- Niche Market Focus: Distributors can learn from Baldor's success by identifying and targeting niche markets that align with their strengths and capabilities. By focusing on specific customer needs and preferences, distributors can differentiate themselves and build a loyal customer base.
- Supply Chain Adaptation: Implementing flexible supply chain strategies, such as split supply chains, can help distributors manage the unique requirements of different product categories. This adaptability is crucial for maintaining efficiency and meeting customer expectations.
- Commitment to Quality and Service: Baldor's commitment to quality and customer service serves as a model for other distributors. By prioritizing customer satisfaction and ensuring that products are delivered in excellent condition, distributors can enhance their reputation and drive business growth.
In summary, Baldor Specialty Foods exemplifies how a focused approach to specialty products, coupled with strategic supply chain management and a commitment to customer service, can lead to success in the competitive food services industry. Other distributors can draw valuable lessons from Baldor's strategies to enhance their own operations and achieve similar success.
What are the Future Trends in Food and Beverage Distribution?
The food and beverage distribution industry is poised for significant transformation in the coming years, driven by technological advancements, evolving consumer expectations, and increasing environmental concerns. This chapter explores the key trends that are expected to shape the future of the industry.
Emerging Trends in Distribution
- Advanced Forecasting and Predictive Analytics: As data becomes more accessible and analytics tools more sophisticated, forecasting will play a crucial role in distribution. Predictive analytics will enable distributors to anticipate demand fluctuations, optimize inventory levels, and enhance supply chain efficiency. This trend is expected to become more prevalent as suppliers increasingly adopt these technologies.
- Integration of Merchandising and Delivery: In the beverage sector, there is a growing trend towards integrating merchandising processes with delivery operations. This integration aims to streamline operations, reduce costs, and improve service levels by ensuring that products are not only delivered efficiently but also displayed effectively in retail environments.
- Centralization and Automation: Centralizing operations and leveraging automation technologies will continue to be a focus for distributors. Automation in warehouses, including the use of robotics and AI-driven systems, will enhance operational efficiency and reduce labor costs. Additionally, centralized data management will facilitate better decision-making and coordination across the supply chain.
Influence of Emerging Technologies
- Autonomous Vehicles: While fully autonomous trucks may still be a few years away, their potential impact on distribution is significant. Autonomous vehicles could revolutionize logistics by reducing labor costs and increasing delivery efficiency. However, challenges remain, particularly in unloading and handling products at delivery points.
- Machine Learning and AI: Machine learning and AI technologies will play a pivotal role in enhancing distribution practices. These technologies can optimize routing, improve demand forecasting, and enable real-time decision-making, leading to more efficient and responsive supply chains.
- Exoskeletons and Workforce Health: The adoption of exoskeletons and other assistive technologies could improve the health and safety of warehouse workers and drivers. By reducing physical strain and injury risks, these technologies can contribute to a healthier and more productive workforce.
Sustainability and Environmental Concerns
- Green Logistics: As environmental concerns grow, distributors will increasingly focus on green logistics practices. This includes adopting electric vehicles, optimizing routes to reduce emissions, and implementing sustainable packaging solutions. Zero-emission zones in urban areas will also drive the adoption of cleaner technologies.
- Sustainable Supply Chain Practices: Distributors will need to consider the environmental impact of their operations and seek ways to minimize their carbon footprint. This may involve collaborating with suppliers to source sustainable products and materials, as well as implementing energy-efficient practices in warehouses and transportation.
Ultimately, the future of food and beverage distribution will be shaped by a combination of technological innovation, integration, and sustainability efforts. As distributors navigate these changes, they will need to embrace new technologies, adapt to evolving consumer expectations, and prioritize environmental responsibility. By staying ahead of these trends, distributors can enhance their competitive edge and contribute to a more sustainable and efficient supply chain.
Conclusion
The food and beverage distribution industry is a dynamic and essential part of the global supply chain, facing a myriad of challenges and opportunities. This guide has explored the industry's complexities, from the foundational roles and responsibilities of distributors to the specific challenges they encounter, such as logistical hurdles and regulatory compliance. By adopting best practices, focusing on customer service, and leveraging technology, distributors can enhance their operational efficiency and service quality.
Technological advancements, particularly in route optimization and visibility solutions, have transformed distribution practices, enabling companies to streamline operations and improve decision-making. The case study of Baldor Specialty Foods highlights the success that can be achieved through a focus on specialty products and customer-centric strategies. As the industry evolves, emerging trends such as advanced forecasting, automation, and sustainability initiatives will continue to shape the future of distribution.
In conclusion, by embracing these insights and strategies, industry professionals can navigate the complexities of the food and beverage distribution sector, driving efficiency, customer satisfaction, and competitive advantage. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource for understanding the current landscape and preparing for the future of food and beverage distribution.
Take the Next Step
Are you ready to transform your food and beverage distribution operations? See our technology in action and experience the difference.